Marriage and Couples
More About Our Research
More About Gottman
Join the Gottman Pro Newsletter
Receive regular updates and clinical resources for professionals from the Gottman Institute.
John Gottman’s concept of “flooding” triggers the “fight or flight” response, risking conflict escalation or emotional disengagement. Subscribe for free resources on managing it in clients.

The infographic below highlights some of Dr. John Gottman’s most notable research findings on marriage and couple relationships. For a more in-depth review of the three phases of Gottman’s research with marriage and couples, continue reading.
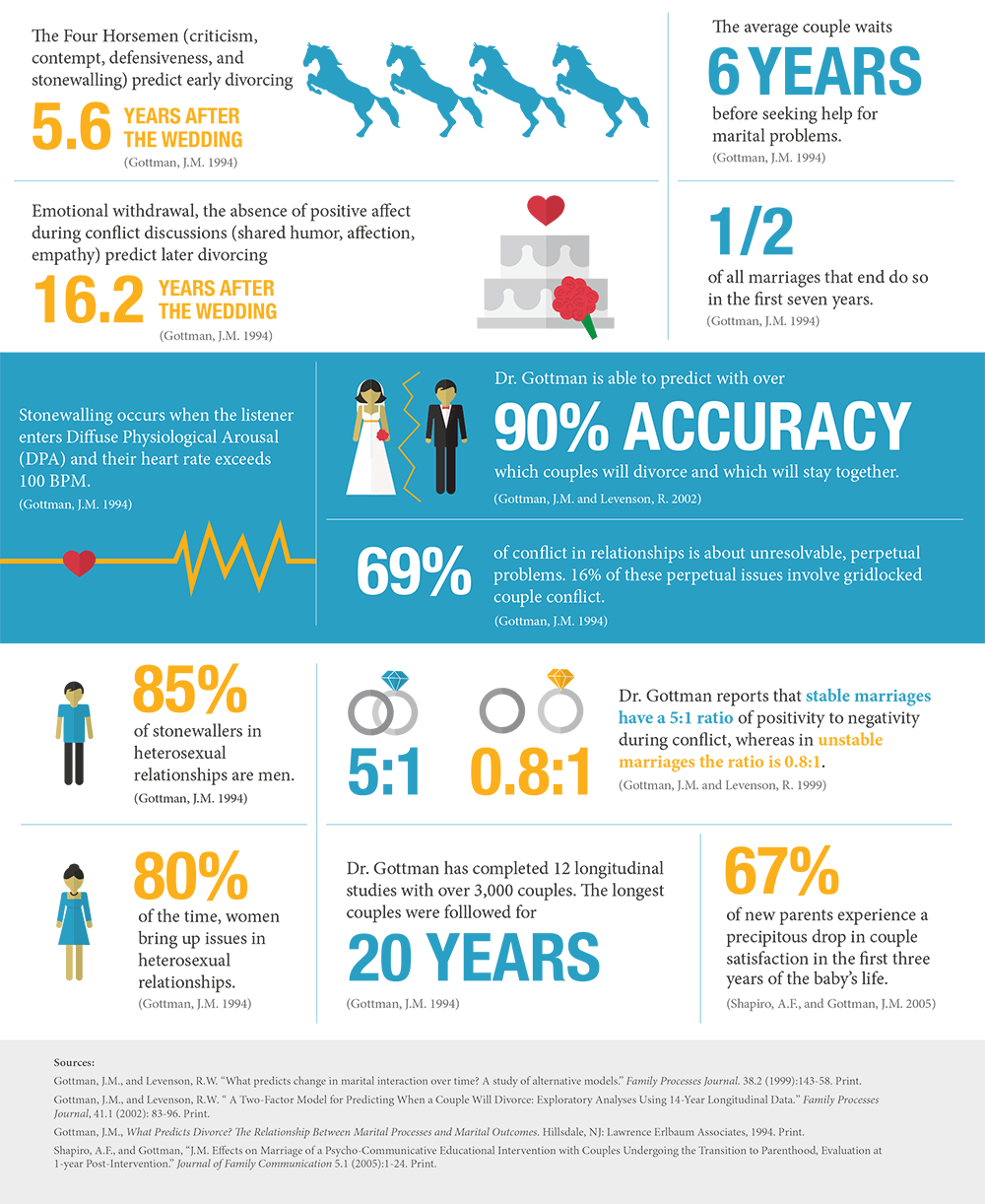
Phase 1: The Discovery of Reliable Patterns of Interaction Discriminating the “Masters” From the “Disasters” of Relationships

In 1976, Dr. Robert Levenson and Dr. John Gottman teamed up to combine the study of emotion with psycho-physiological measurement and a video-recall method that gave us rating dial measures (still applying game theory) of how people felt during conflict. This was the new way of getting the “talk table” numbers. The research also became longitudinal. They made no predictions in the first study, but they were interested in a measure of “physiological linkage,” because a prior study showed that the skin conductance of two nurses was correlated only if they disliked one another. They thought that might be linked to negative affect in couples. Indeed it was.
They were also amazed that in their first study with 30 couples they were able to “predict” the change in marital satisfaction almost perfectly with their physiological measures. The results revealed that the more physiologically aroused couples were (in all channels, including heart rate, skin conductance, gross motor activity, and blood velocity), the more their marriages deteriorated in happiness over a three-year period, even controlling the initial level of marital satisfaction.
The rating dial and their observational coding of the interaction also “predicted” changes in relationship satisfaction. Such large correlations in the data were unprecedented. Furthermore, Gottman and Levenson had preceded the conflict conversation with a reunion conversation (in which couples talked about the events of their day before the conflict discussion), and they had followed the conflict discussion with a positive topic. Gottman and Levenson were amazed to discover that harsh startup by women in the conflict discussion was predictable by the male partner’s disinterest or irritability in the events of the day discussion. They found that the quality of the couple’s friendship, especially as maintained by men, was critical in understanding conflict. Furthermore, the ability to rebound from, or “repair”, conflict to the positive conversation became a marker of emotion regulation ability of couples.
Both Levenson and Gottman had discovered Dr. Paul Ekman and Dr. Wallace Friesen’s Facial Affect Coding System (FACS), and Gottman subsequently developed the Specific Affect Coding System (SPAFF), which was an integration of FACS and earlier systems in the Gottman lab.
The SPAFF became the main system that Gottman used to code couples’ interaction. At first, it took 25 hours to code 15 minutes of interaction, but later Gottman was able to get the same coding done in just 45 minutes, with no loss of reliability. Gottman also began applying time-series analysis to the analysis of interaction data. He wrote, Time-Series Analysis: A Comprehensive Introduction for Social Scientists, a book on time-series analysis to explain these methods to psychologists, and developed some new methods for analyzing dominance and bi-directionality with James Ringland.
Phase 2: Prediction and the Replication of the Prediction

Soon after, Gottman and Levenson received their first grant together and began attempting to replicate their observations from the first study. The subsequent studies they conducted in their labs with colleagues eventually spanned the entire life course — with the longest of the studies following couples for 20 years, in Levenson’s Berkeley lab.
The Gottman lab at the University of Illinois also studied the linkages between marital interaction, parenting, and children’s social development with Dr. Lynn Katz, and later at the University of Washington involved studying these linkages with infants with Dr. Alyson Shapiro. Gottman developed the concept of “meta-emotion”, which is how people feel about emotion (such as specific emotions like anger), emotional expression, and emotional understanding in general. Meta-emotion mismatches between parents in that study predicted divorce with 80% accuracy.
Gottman and Levenson discovered that couples interaction had enormous stability over time (about 80% stability in conflict discussions separated by 3 years). They also discovered that most relationship problems (69%) never get resolved but are “perpetual problems” based on personality differences between partners.
In seven longitudinal studies, one with violent couples (with Neil Jacobson), the predictions replicated. Gottman could predict whether a couple would divorce with an average of over 90% accuracy, across studies using the ratio of positive to negative SPAFF codes, the Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse (Criticism, Defensiveness, Contempt, and Stonewalling), physiology, the rating dial, and an interview they devised, the Oral History Interview, as coded by Kim Buehlman’s coding system.
Gottman could predict whether or not their stable couples would be happy or unhappy using measures of positive affect during conflict. With Dr. Jim Coan, he discovered that positive affect was used not randomly, but to physiologically soothe the partner. Gottman also discovered that in heterosexual relationships, men accepting influence from their wives was predictive of happy and stable marriages. Bob Levenson also discovered that humor was physiologically soothing and that empathy had a physiological substrate (in research with Dr. Anna Ruef), using the rating dial.
Phase 3: Theory Building, Understanding, and Prevention & Intervention

The third phase of Gottman’s research program was devoted to trying to understand the empirical predictions, and thus building and then testing theory. Ultimately, Gottman aimed to build a theory that was testable or disconfirmable.
Testing theory in the psychological field requires clinical interventions. In 1996, the Gottman lab returned to intervention research with Dr. Julie Schwartz Gottman. John and Julie Gottman designed both proximal and distal change studies. In a proximal change study, one intervenes briefly with interventions designed only to make the second of two conflict discussions less divorce-prone. In one of these studies, they discovered that a 20-minute break, in which couples stopped talking and just read magazines (as their heart rates returned to baseline), dramatically changed the discussion, so that people had access to their sense of humor and affection.
Together with Julie, John Gottman started building the Sound Relationship House Theory. That theory became the basis of the design of clinical interventions for couples in John Gottman’s book, The Marriage Clinic, and Julie Gottman’s book, The Marriage Clinic Casebook. In August of 1996, they founded The Gottman Institute to continue to develop evidence-based approaches to improving couples therapy outcomes.
Read more about The Gottman Institute’s mission here.